Purpose & Intended Use
The overall purpose of the ontology is to provide a high level model for documenting plans that can be described as a series of sequential inputs and outputs of steps in a form of acyclic graphs. The ontology also covers the modelling of the instantiation of plans (e.g. an execution trace of a workflow), which is achieved via tight alignment with the PROV-O ontology. Such descriptions are useful for documenting the expected and the actual behaviour of complex data processing systems (e.g. an IoT infrastructure), scientific experiments (e.g. an executable scientific workflows), as well as various protocols that are to date predominately stored in its paper form (e.g. a lab protocol of an experiment).
The EP-PLAN vocabulary is intended for documenting the expected and actual behaviour of arbitrary systems, however, the plan elements are not strictly designed to guide the execution of processes (e.g. within a scientific workflow platform). The ontology is expected to be useful for scientists and developers, who wish to enhance the transparency of protocols and computational systems through the means of providing meta descriptions, which can be queried by both human users and automated agents. We foresee the main application of the ontology in scenarios where information about systems is sought to facilitate data integration and reuse, pattern mining, and assessments (e.g. trust, privacy, security, quality, etc.).
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to cite this resource
Markovic, M., Garijo, D., Edwards, P., Vasconcelos, W., EP-Plan: Linking Abstract Plans with Execution Traces, April 2019, https://w3id.org/ep-plan.Related Publications
- Using Knowledge Graphs to Unlock Practical Collection, Integration, and Audit of AI Accountability Information., Naja I., Markovic M., Edwards P., Pang W., Cottrill C., Williams R., IEEE Access. 2022 Jul 6;10:74383-411.
- The Accountability Fabric: A Suite of Semantic Tools For Managing AI System Accountability and Audit., Markovic M., Naja I., Edwards P., Pang W., In Proceedings of the ISWC 2021 Posters, Demos and Industry Tracks: From Novel Ideas to Industrial Practice co-located with 20th International Semantic Web Conference (ISWC 2021), 2021.
- A semantic framework to support AI system accountability and audit., Naja I., Markovic M., Edwards P., Cottrill C., In The Semantic Web: 18th International Conference, ESWC 2021, Virtual Event, June 6–10, 2021, Proceedings 18 2021 (pp. 160-176). Springer International Publishing
- Semantic Modelling of Plans and Execution Traces for Enhancing Transparency of IoT Systems, M Markovic, D Garijo, P Edwards, W Vasconcelos, In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Internet of Things: Systems, Management and Security (IOTSMS) , 2019
- Linking Abstract Plans of Scientific Experiments to their Corresponding Execution Traces, Markovic M., Garijo D., Edwards P., In Proceedings of the Third International Workshop on Capturing Scientific Knowledge (Sciknow 2019), 2019
- Enhancing Transparency of MQTT Brokers For IoT Applications Through Provenance Streams, Markovic M., Edwards P., In M4IoT '19: Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Middleware and Applications for the Internet of Things, 2019
Overview
The EP-PLAN ontology builds on two pre-existing ontologies, namely P-PLAN and W3C recommendation PROV-O.Competency Questions
A list of competency questions and example SPARQL queries is available here
Examples
Sample Datasets
See below for available sample datasets
Prefixes
| Prefix | URI |
|---|---|
| ep-plan | <https://w3id.org/ep-plan#> |
| prov | <http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#> |
| odrl | <http://www.w3.org/ns/odrl/2/> | eli | <http://data.europa.eu/eli/ontology#> | gdpr | <https://w3id.org/GDPRtEXT/gdpr#> | gdprText | <https://w3id.org/GDPRtEXT#> |
Basic plan structure
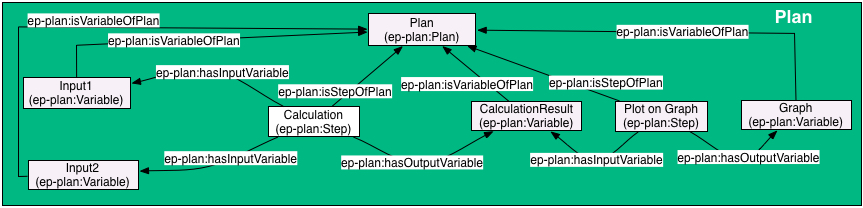
Example: Using steps and variables to describe plans
Mapping execution trace
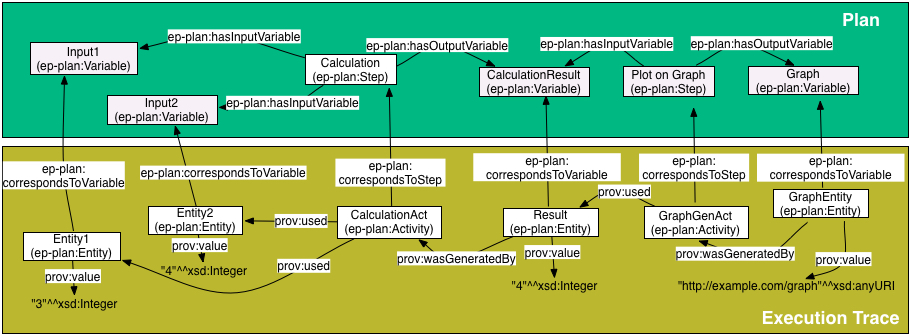
Example: Mapping activities and entities to steps and variables
Execution Trace Bundles
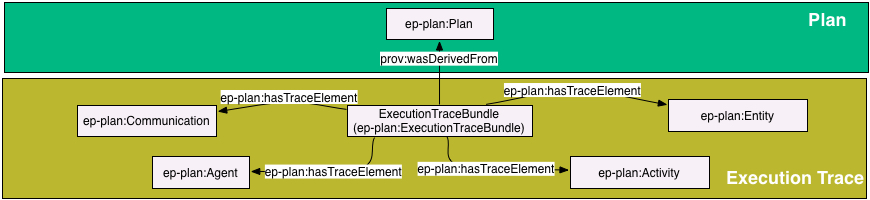
Example: Keeping everything in one graph
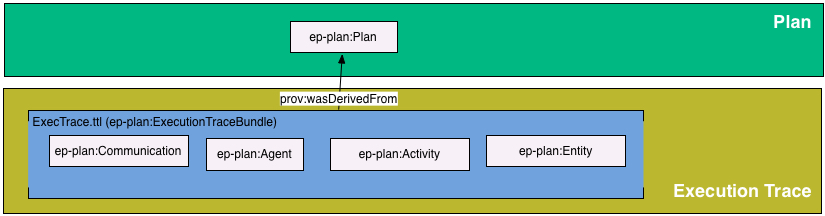
Example: Using separate documents as bundles
Example: Recording the main execution activity

Constraints
Example: Associating constraints with different plan elements

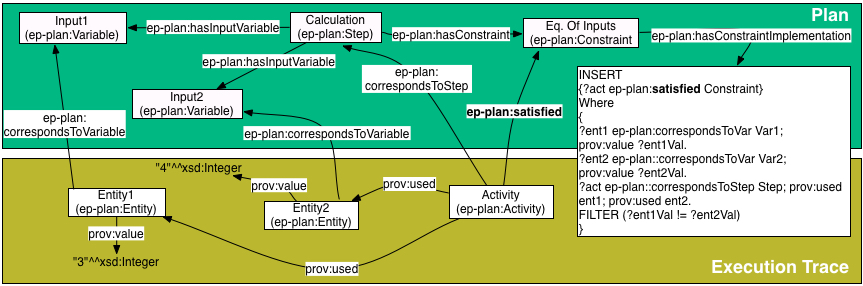
Example: Associating constraints with steps
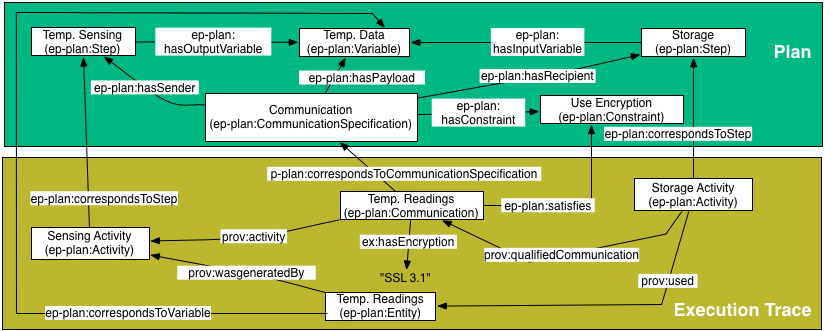
Example: Associating constraints with communication specification
Policies, Rationales and Objectives
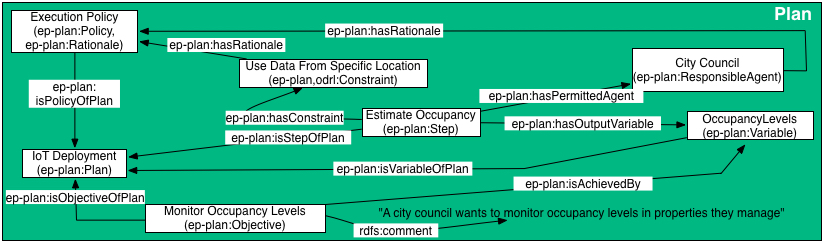
Example: Associating policies with plans and linking to other plan elements
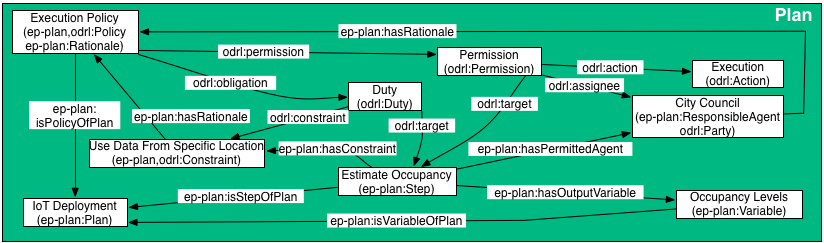
Example: A policy description expanded using the W3C ODRL vocabulary
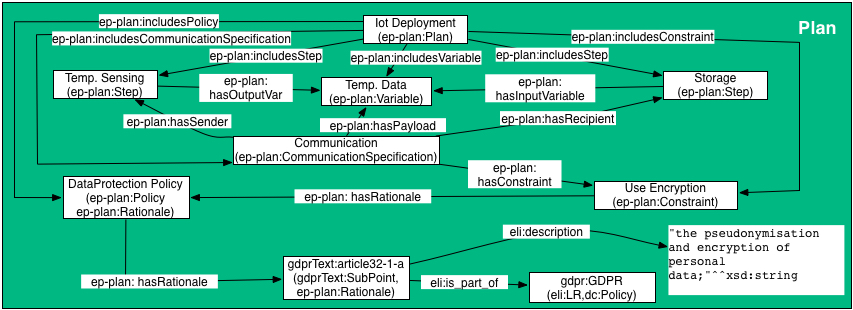
Example: A policy linked to a GDPR article
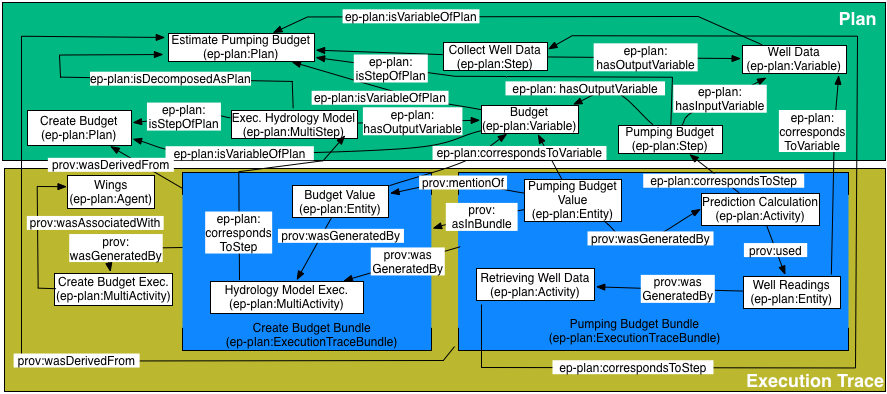
Plan decomposition
Example: Use of MultiVariable
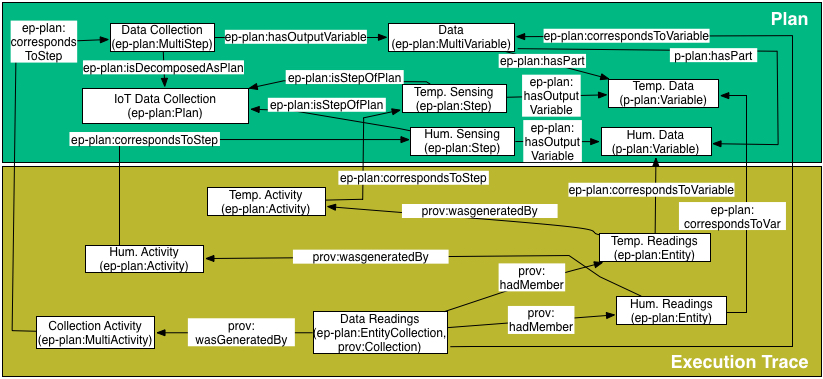
Example: Extending descriptions using the W3C SSN vocabulary
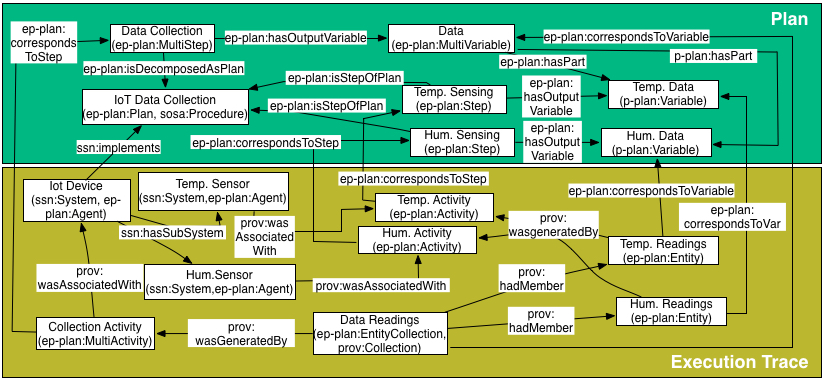
Example: Linking executions of different abstractions of a plan>

Mapping execution trace
Example: Mapping activities and entities to steps and variables

Execution Trace Bundles
Example: Keeping everything in one graph

Example: Using separate documents as bundles

Example: Recording the main execution activity

Constraints
Example: Associating constraints with different plan elements

Example: Associating constraints with steps

Example: Associating constraints with communication specification

Policies, Rationales and Objectives
Example: Associating policies with plans and linking to other plan elements

Example: A policy description expanded using the W3C ODRL vocabulary

Example: A policy linked to a GDPR article

Plan decomposition
Example: Use of MultiVariable

Example: Extending descriptions using the W3C SSN vocabulary

Example: Linking executions of different abstractions of a plan>


Execution Trace Bundles
Example: Keeping everything in one graph

Example: Using separate documents as bundles

Example: Recording the main execution activity

Constraints
Example: Associating constraints with different plan elements

Example: Associating constraints with steps

Example: Associating constraints with communication specification

Policies, Rationales and Objectives
Example: Associating policies with plans and linking to other plan elements

Example: A policy description expanded using the W3C ODRL vocabulary

Example: A policy linked to a GDPR article

Plan decomposition
Example: Use of MultiVariable

Example: Extending descriptions using the W3C SSN vocabulary

Example: Linking executions of different abstractions of a plan>


Example: Using separate documents as bundles

Example: Recording the main execution activity

Constraints
Example: Associating constraints with different plan elements

Example: Associating constraints with steps

Example: Associating constraints with communication specification

Policies, Rationales and Objectives
Example: Associating policies with plans and linking to other plan elements

Example: A policy description expanded using the W3C ODRL vocabulary

Example: A policy linked to a GDPR article

Plan decomposition
Example: Use of MultiVariable

Example: Extending descriptions using the W3C SSN vocabulary

Example: Linking executions of different abstractions of a plan>


Example: Recording the main execution activity

Constraints
Example: Associating constraints with different plan elements

Example: Associating constraints with steps

Example: Associating constraints with communication specification

Policies, Rationales and Objectives
Example: Associating policies with plans and linking to other plan elements

Example: A policy description expanded using the W3C ODRL vocabulary

Example: A policy linked to a GDPR article

Plan decomposition
Example: Use of MultiVariable

Example: Extending descriptions using the W3C SSN vocabulary

Example: Linking executions of different abstractions of a plan>


Constraints
Example: Associating constraints with different plan elements

Example: Associating constraints with steps

Example: Associating constraints with communication specification

Policies, Rationales and Objectives
Example: Associating policies with plans and linking to other plan elements

Example: A policy description expanded using the W3C ODRL vocabulary

Example: A policy linked to a GDPR article

Plan decomposition
Example: Use of MultiVariable

Example: Extending descriptions using the W3C SSN vocabulary

Example: Linking executions of different abstractions of a plan>


Example: Associating constraints with steps

Example: Associating constraints with communication specification

Policies, Rationales and Objectives
Example: Associating policies with plans and linking to other plan elements

Example: A policy description expanded using the W3C ODRL vocabulary

Example: A policy linked to a GDPR article

Plan decomposition
Example: Use of MultiVariable

Example: Extending descriptions using the W3C SSN vocabulary

Example: Linking executions of different abstractions of a plan>


Example: Associating constraints with communication specification

Policies, Rationales and Objectives
Example: Associating policies with plans and linking to other plan elements

Example: A policy description expanded using the W3C ODRL vocabulary

Example: A policy linked to a GDPR article

Plan decomposition
Example: Use of MultiVariable

Example: Extending descriptions using the W3C SSN vocabulary

Example: Linking executions of different abstractions of a plan>

